Flooding is one of the most devastating natural disasters that can strike any area, leading to extensive damage to property, infrastructure, and even loss of life. While the causes of flooding can be varied, one critical factor that significantly impacts its severity is the presence and functionality of drainage systems. Proper drainage systems play a pivotal role in mitigating the effects of floods and are crucial in managing stormwater effectively. This article delves into why having a well-designed and maintained drainage system is essential for preventing flooding and ensuring community resilience.
Understanding Drainage Systems
Drainage systems are engineered networks designed to manage and direct the flow of water from rainfall, melting snow, or other sources away from buildings, streets, and other vulnerable areas. These systems help prevent water accumulation and overflow that can lead to flooding. They typically consist of various components such as gutters, downspouts, storm sewers, and retention ponds.
Why Proper Drainage Is Crucial
- Prevents Property Damage
One of the most immediate benefits of an efficient drainage system is the protection it offers against property damage. When water is not properly directed away from structures, it can seep into foundations, walls, and basements. Over time, this can lead to serious issues like mold growth, structural weakening, and costly repairs. A well-designed drainage system helps prevent these problems by ensuring that excess water is safely diverted away from buildings. - Reduces Erosion
Erosion is another significant issue that can result from inadequate drainage. When water runs off in uncontrolled amounts, it can erode soil, leading to the loss of valuable topsoil and damage to landscaping. This not only affects the aesthetic value of properties but can also impact agricultural productivity. Effective drainage systems help manage runoff and reduce erosion by channeling water away from areas prone to soil degradation. - Minimizes Flood Risk
Proper drainage systems are critical in minimizing the risk of flooding, especially in urban areas where impervious surfaces like roads and pavements prevent water from soaking into the ground. Inadequate drainage can lead to the accumulation of stormwater, which increases the risk of flash floods and prolonged flooding events. By efficiently directing water away from high-risk areas, drainage systems play a key role in flood prevention. - Protects Public Infrastructure
Drainage systems are vital for protecting public infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and public buildings. Excessive water accumulation can lead to road damage, bridge failures, and disruptions in public services. Well-maintained drainage systems help safeguard these critical structures, ensuring they remain functional and safe for public use. - Improves Health and Safety
Stagnant water due to poor drainage can create breeding grounds for mosquitoes and other pests, leading to health risks such as vector-borne diseases. By efficiently draining water away, these systems help reduce the likelihood of such health hazards. Additionally, avoiding waterlogging and flooding reduces the risk of accidents and injuries related to slippery or obstructed pathways.
Types of Drainage Systems
- Surface Drainage
Surface drainage involves managing water that collects on the surface of the ground. This is achieved through systems like gutters, ditches, and swales, which collect and direct water away from areas where it could cause flooding or damage. Surface drainage is particularly important for preventing water from accumulating on roads and driveways. - Subsurface Drainage
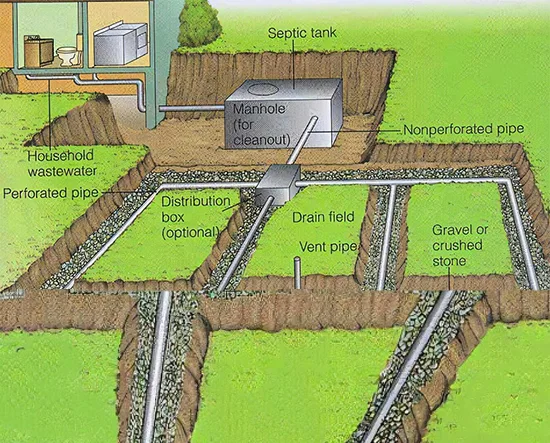
Subsurface drainage systems are designed to manage groundwater and prevent water from saturating the soil beneath the surface. This is typically achieved through the use of perforated pipes or drains installed below ground level. Subsurface drainage helps protect foundations and prevent soil instability. - Stormwater Management
Stormwater management involves controlling and treating water runoff from rainfall to prevent flooding and protect water quality. This can include the use of retention and detention basins, which temporarily store stormwater and release it slowly to reduce peak flow rates. Proper stormwater management helps balance the natural water cycle and mitigate flood risks.
Key Components of an Effective Drainage System
- Gutters and Downspouts
Gutters and downspouts are essential for collecting rainwater from roofs and directing it away from the foundation of buildings. Properly installed gutters help prevent water from overflowing and causing damage to the structure. Downspouts should be positioned to discharge water at a safe distance from the foundation. - Storm Sewers
Storm sewers are designed to carry large volumes of stormwater away from urban areas. They consist of a network of pipes and drainage channels that transport water to appropriate discharge points, such as rivers or treatment facilities. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure that storm sewers remain clear and functional. - Retention and Detention Ponds
Retention and detention ponds are used to manage stormwater runoff by capturing and storing it temporarily. Retention ponds hold water indefinitely, while detention ponds are designed to release it slowly over time. These ponds help reduce the risk of downstream flooding and provide opportunities for water recycling. - French Drains
French drains are a type of subsurface drainage system that consists of a perforated pipe surrounded by gravel or rock. They are effective for managing groundwater and preventing water from pooling around foundations. French drains are particularly useful in areas with high water tables or poor soil drainage.
Maintaining Drainage Systems
Proper maintenance of drainage systems is essential to ensure their effectiveness and longevity. Regular inspections should be conducted to identify and address potential issues such as blockages, leaks, or damage. Cleaning gutters, clearing storm drains, and checking the condition of pipes are all important maintenance tasks. Additionally, ensuring that landscaping and construction activities do not obstruct drainage pathways is crucial for maintaining system functionality.
The Role of Community and Policy
Effective flood prevention and drainage management require a collaborative approach involving communities, governments, and planners. Communities should be educated about the importance of proper drainage and encouraged to participate in maintenance efforts. Local governments play a crucial role in implementing and enforcing regulations related to drainage infrastructure and floodplain management. Urban planners and developers should integrate effective drainage solutions into new construction projects to prevent future flooding issues.
Conclusion
Proper drainage systems are indispensable for preventing flooding and managing stormwater effectively. They protect property, reduce erosion, minimize flood risk, safeguard public infrastructure, and improve health and safety. By understanding the various types of drainage systems and their key components, individuals and communities can better appreciate their importance and take proactive measures to ensure their functionality. Regular maintenance, community involvement, and supportive policies are all critical elements in maintaining effective drainage systems and protecting against the devastating impacts of flooding. Investing in robust drainage infrastructure not only helps prevent immediate damage but also contributes to long-term resilience and sustainability for future generations.